Rate-limiting is a process that is used to define the rate at which consumers can access APIs. Also, it determines the speed at which a consumer can access APIs. Rate limit is calculated in real time.
Rate-limiting is applicable to resources. For example, in the following endpoint URL, "http://endpointurl/products", "/products" is a resource. It can be configured or over-ridden resource level.
You can add rate limits to API resources for the SLA plans to which the APIs are subscribed. Once the API exceeds the rate limit, the subscriber gets Status 429 message in the response header. Status 429 message indicates that the rate-limit has crossed.
For more information on adding rate limits to API resources, refer Adding rate limits to API resources section in Publisher document. Publisher assigns multiple plans for APIs while publishing them. Subscriber can select one of the plans while consuming APIs.
Administrators and publishers of API manager can use rate limiting to define the number of API requests per second/minute/hour. For example, if you set the rate as 5 req/sec, the speed at which a consumer can access each API can be high.
If API Manager is deployed in a cluster, the rate-limit is considered across the nodes. The consumer gets an error message whenever the defined limit is crossed within a single node or across a combination of nodes.
In API manager, two types of algorithms can be used to limit the rate: Rolling and Fixed.
In fixed window algorithm, the period is considered from the starting of the time unit to the end of the time unit. For example, a period is considered as 0-60 seconds for a minute irrespective of the time frame at which the API request has been made.
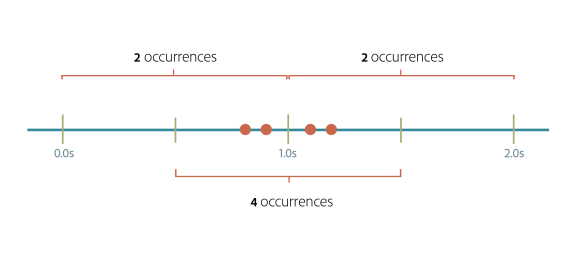
In rolling window algorithm, the period is considered from the fraction of the time at which the request has been made to the end of the time unit. For example, if two requests for API calls are made at 30th second and 40th second of a minute it is considered as two requests from 30th second of that minute up to the 30th second of next minute.
Consider an illustration as follows: