#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv_modules.hpp>
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_VIZ
#endif
static const char* keys =
{ "{@images_list | | Image list where the captured pattern images are saved}"
"{@calib_param_path | | Calibration_parameters }"
"{@proj_width | | The projector width used to acquire the pattern }"
"{@proj_height | | The projector height used to acquire the pattern}"
"{@white_thresh | | The white threshold height (optional)}"
"{@black_thresh | | The black threshold (optional)}" };
static void help()
{
cout << "\nThis example shows how to use the \"Structured Light module\" to decode a previously acquired gray code pattern, generating a pointcloud"
"\nCall:\n"
"./example_structured_light_pointcloud <images_list> <calib_param_path> <proj_width> <proj_height> <white_thresh> <black_thresh>\n"
<< endl;
}
static bool readStringList( const string& filename, vector<string>& l )
{
l.resize( 0 );
FileStorage fs( filename, FileStorage::READ );
if( !fs.isOpened() )
{
cerr << "failed to open " << filename << endl;
return false;
}
FileNode n = fs.getFirstTopLevelNode();
if( n.type() != FileNode::SEQ )
{
cerr << "cam 1 images are not a sequence! FAIL" << endl;
return false;
}
FileNodeIterator it = n.begin(), it_end = n.end();
for( ; it != it_end; ++it )
{
l.push_back( ( string ) *it );
}
n = fs["cam2"];
if( n.type() != FileNode::SEQ )
{
cerr << "cam 2 images are not a sequence! FAIL" << endl;
return false;
}
it = n.begin(), it_end = n.end();
for( ; it != it_end; ++it )
{
l.push_back( ( string ) *it );
}
if( l.size() % 2 != 0 )
{
cout << "Error: the image list contains odd (non-even) number of elements\n";
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(
int argc,
char** argv )
{
CommandLineParser parser( argc, argv, keys );
params.width = parser.get<
int>( 2 );
params.height = parser.get<
int>( 3 );
if( images_file.empty() || calib_file.empty() ||
params.width < 1 ||
params.height < 1 || argc < 5 || argc > 7 )
{
help();
return -1;
}
Ptr<structured_light::GrayCodePattern> graycode = structured_light::GrayCodePattern::create(
params );
size_t white_thresh = 0;
size_t black_thresh = 0;
if( argc == 7 )
{
white_thresh = parser.get<unsigned>( 4 );
black_thresh = parser.get<unsigned>( 5 );
graycode->setWhiteThreshold( white_thresh );
graycode->setBlackThreshold( black_thresh );
}
vector<string> imagelist;
bool ok = readStringList( images_file, imagelist );
if( !ok || imagelist.empty() )
{
cout << "can not open " << images_file << " or the string list is empty" << endl;
help();
return -1;
}
FileStorage fs( calib_file, FileStorage::READ );
if( !fs.isOpened() )
{
cout << "Failed to open Calibration Data File." << endl;
help();
return -1;
}
Mat cam1intrinsics, cam1distCoeffs, cam2intrinsics, cam2distCoeffs, R, T;
fs["cam1_intrinsics"] >> cam1intrinsics;
fs["cam2_intrinsics"] >> cam2intrinsics;
fs["cam1_distorsion"] >> cam1distCoeffs;
fs["cam2_distorsion"] >> cam2distCoeffs;
fs["R"] >> R;
fs["T"] >> T;
cout << "cam1intrinsics" << endl << cam1intrinsics << endl;
cout << "cam1distCoeffs" << endl << cam1distCoeffs << endl;
cout << "cam2intrinsics" << endl << cam2intrinsics << endl;
cout << "cam2distCoeffs" << endl << cam2distCoeffs << endl;
cout << "T" << endl << T << endl << "R" << endl << R << endl;
if( (!R.data) || (!T.data) || (!cam1intrinsics.data) || (!cam2intrinsics.data) || (!cam1distCoeffs.data) || (!cam2distCoeffs.data) )
{
cout << "Failed to load cameras calibration parameters" << endl;
help();
return -1;
}
size_t numberOfPatternImages = graycode->getNumberOfPatternImages();
vector<vector<Mat> > captured_pattern;
captured_pattern.resize( 2 );
captured_pattern[0].resize( numberOfPatternImages );
captured_pattern[1].resize( numberOfPatternImages );
Size imagesSize = color.size();
cout << "Rectifying images..." << endl;
Mat R1, R2, P1, P2, Q;
stereoRectify( cam1intrinsics, cam1distCoeffs, cam2intrinsics, cam2distCoeffs, imagesSize, R, T, R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, 0,
-1, imagesSize, &validRoi[0], &validRoi[1] );
Mat map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y;
for( size_t i = 0; i < numberOfPatternImages; i++ )
{
if( (!captured_pattern[0][i].data) || (!captured_pattern[1][i].data) )
{
cout << "Empty images" << endl;
help();
return -1;
}
}
cout << "done" << endl;
vector<Mat> blackImages;
vector<Mat> whiteImages;
blackImages.resize( 2 );
whiteImages.resize( 2 );
cout << endl << "Decoding pattern ..." << endl;
Mat disparityMap;
bool decoded = graycode->decode( captured_pattern, disparityMap, blackImages, whiteImages,
if( decoded )
{
cout << endl << "pattern decoded" << endl;
Mat cm_disp, scaledDisparityMap;
cout <<
"disp min " <<
min << endl <<
"disp max " <<
max << endl;
imshow(
"cm disparity m", cm_disp );
Mat pointcloud;
disparityMap.convertTo( disparityMap,
CV_32FC1 );
Mat dst, thresholded_disp;
imshow(
"threshold disp otsu", dst );
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_VIZ
Mat pointcloud_tresh, color_tresh;
pointcloud.copyTo( pointcloud_tresh, thresholded_disp );
color.copyTo( color_tresh, thresholded_disp );
viz::Viz3d myWindow( "Point cloud with color" );
myWindow.setBackgroundMeshLab();
myWindow.showWidget( "coosys", viz::WCoordinateSystem() );
myWindow.showWidget( "pointcloud", viz::WCloud( pointcloud_tresh, color_tresh ) );
myWindow.showWidget(
"text2d", viz::WText(
"Point cloud",
Point(20, 20), 20, viz::Color::green() ) );
myWindow.spin();
#endif
}
return 0;
}
MatExpr max(const Mat &a, const Mat &b)
MatExpr min(const Mat &a, const Mat &b)
void reprojectImageTo3D(InputArray disparity, OutputArray _3dImage, InputArray Q, bool handleMissingValues=false, int ddepth=-1)
Reprojects a disparity image to 3D space.
void stereoRectify(InputArray cameraMatrix1, InputArray distCoeffs1, InputArray cameraMatrix2, InputArray distCoeffs2, Size imageSize, InputArray R, InputArray T, OutputArray R1, OutputArray R2, OutputArray P1, OutputArray P2, OutputArray Q, int flags=CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY, double alpha=-1, Size newImageSize=Size(), Rect *validPixROI1=0, Rect *validPixROI2=0)
Computes rectification transforms for each head of a calibrated stereo camera.
void initUndistortRectifyMap(InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray distCoeffs, InputArray R, InputArray newCameraMatrix, Size size, int m1type, OutputArray map1, OutputArray map2)
Computes the undistortion and rectification transformation map.
void convertScaleAbs(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, double alpha=1, double beta=0)
Scales, calculates absolute values, and converts the result to 8-bit.
void minMaxIdx(InputArray src, double *minVal, double *maxVal=0, int *minIdx=0, int *maxIdx=0, InputArray mask=noArray())
Finds the global minimum and maximum in an array.
@ BORDER_CONSTANT
iiiiii|abcdefgh|iiiiiii with some specified i
Definition: core/include/opencv2/core/base.hpp:269
Rect2i Rect
Definition: modules/core/include/opencv2/core/types.hpp:496
Point2i Point
Definition: modules/core/include/opencv2/core/types.hpp:209
std::string String
Definition: cvstd.hpp:149
Size2i Size
Definition: modules/core/include/opencv2/core/types.hpp:370
Scalar_< double > Scalar
Definition: modules/core/include/opencv2/core/types.hpp:709
#define CV_32FC1
Definition: core/include/opencv2/core/hal/interface.h:118
void imshow(const String &winname, InputArray mat)
Displays an image in the specified window.
int waitKey(int delay=0)
Waits for a pressed key.
@ IMREAD_GRAYSCALE
If set, always convert image to the single channel grayscale image (codec internal conversion).
Definition: imgcodecs.hpp:70
@ IMREAD_COLOR
Same as IMREAD_COLOR_BGR.
Definition: imgcodecs.hpp:72
CV_EXPORTS_W Mat imread(const String &filename, int flags=IMREAD_COLOR_BGR)
Loads an image from a file.
void cvtColor(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int code, int dstCn=0, AlgorithmHint hint=cv::ALGO_HINT_DEFAULT)
Converts an image from one color space to another.
@ COLOR_RGB2GRAY
Definition: imgproc/include/opencv2/imgproc.hpp:556
void applyColorMap(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int colormap)
Applies a GNU Octave/MATLAB equivalent colormap on a given image.
@ COLORMAP_JET
Definition: imgproc/include/opencv2/imgproc.hpp:4477
double threshold(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, double thresh, double maxval, int type)
Applies a fixed-level threshold to each array element.
@ THRESH_BINARY
Definition: imgproc/include/opencv2/imgproc.hpp:325
@ THRESH_OTSU
flag, use Otsu algorithm to choose the optimal threshold value
Definition: imgproc/include/opencv2/imgproc.hpp:331
@ DECODE_3D_UNDERWORLD
Kyriakos Herakleous, Charalambos Poullis. "3DUNDERWORLD-SLS: An Open-Source Structured-Light Scanning...
Definition: structured_light/structured_light.hpp:56
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
Definition: highgui_qt.cpp:3
kinfu::Params Params
DynamicFusion implementation.
Definition: dynafu.hpp:44
PyParams params(const std::string &tag, const std::string &model, const std::string &weights, const std::string &device)
Definition: core/include/opencv2/core.hpp:107
First of all the needed parameters must be passed to the program. The first is the name list of previously acquired pattern images, stored in a .yaml file organized as below:
For example, the dataset used for this tutorial has been acquired using a projector with a resolution of 1280x800, so 42 pattern images (from number 1 to 42) + 1 white (number 43) and 1 black (number 44) were captured with both the two cameras.
Then the cameras calibration parameters, stored in another .yml file, together with the width and the height of the projector used to project the pattern, and, optionally, the values of white and black tresholds, must be passed to the tutorial program.
If the white and black thresholds are passed as parameters (these thresholds influence the number of decoded pixels), their values can be set, otherwise the algorithm will use the default values.
As regards the black and white images, they must be stored in two different vectors of Mat:
It is important to underline that all the images, the pattern ones, black and white, must be loaded as grayscale images and rectified before being passed to decode method:
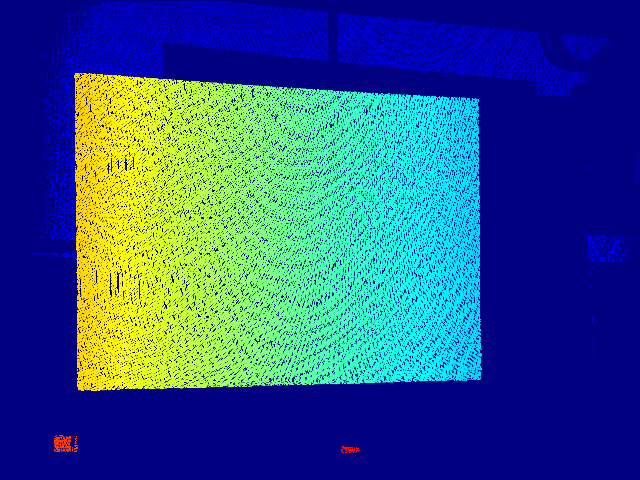
To better visualize the result, a colormap is applied to the computed disparity:
At this point the point cloud can be generated using the reprojectImageTo3D method, taking care to convert the computed disparity in a CV_32FC1 Mat (decode method computes a CV_64FC1 disparity map):
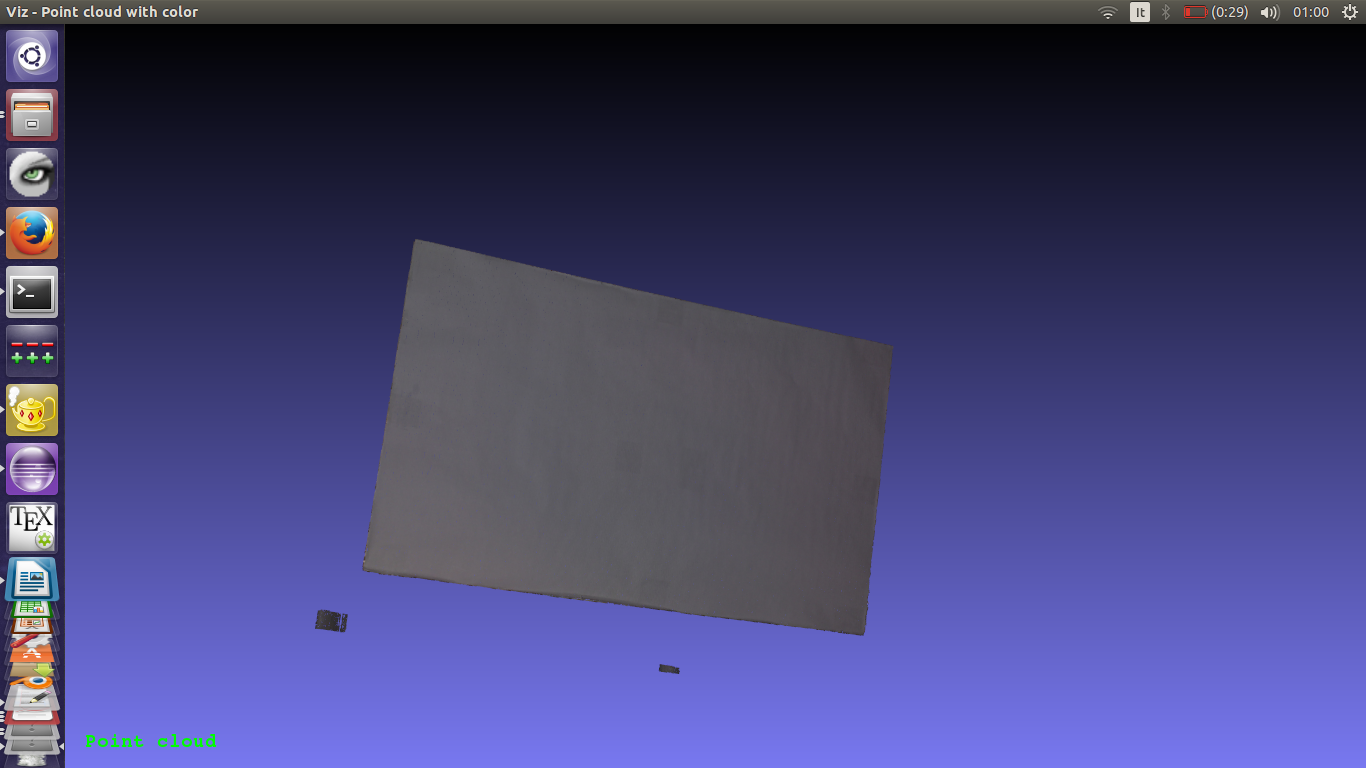
The white image of cam1 was previously loaded also as a color image, in order to map the color of the object on its reconstructed pointcloud:
The background renoval mask is thus applied to the point cloud and to the color image:
Finally the computed point cloud of the scanned object can be visualized on viz: